
Double digit percentage annual CO2 emission cuts
The consequence of
There is little discussion of these basic points, which strongly suggests widespread denial across society.
- the physics of climate change,
- the international commitments given, and
- the lack of effective action so far
The physics of climate change is that as CO2 builds up in the atmosphere, global warming steadily increases.
The key international agreement on climate change is the Paris Agreement, which commits countries to pursue efforts to keep global warming to within 1.5°C - see document 113.
The physics and maths of emission cuts
It has long been known that as CO2 is added to the atmosphere, the concentration builds up, and the average temperature rises. So if we want to keep global warming to within a particular limit, the total emissions of CO2 has to be limited. The amount of CO2 that can still be emitted is know as the CO2 budget, or carbon budget. Annual CO2 emissions have to be cut to stay within this total limit. The sooner the cuts start, the less drastic the cuts need to be. This chart [1] was published in 2018 in the Global Carbon Budget 2018 [2].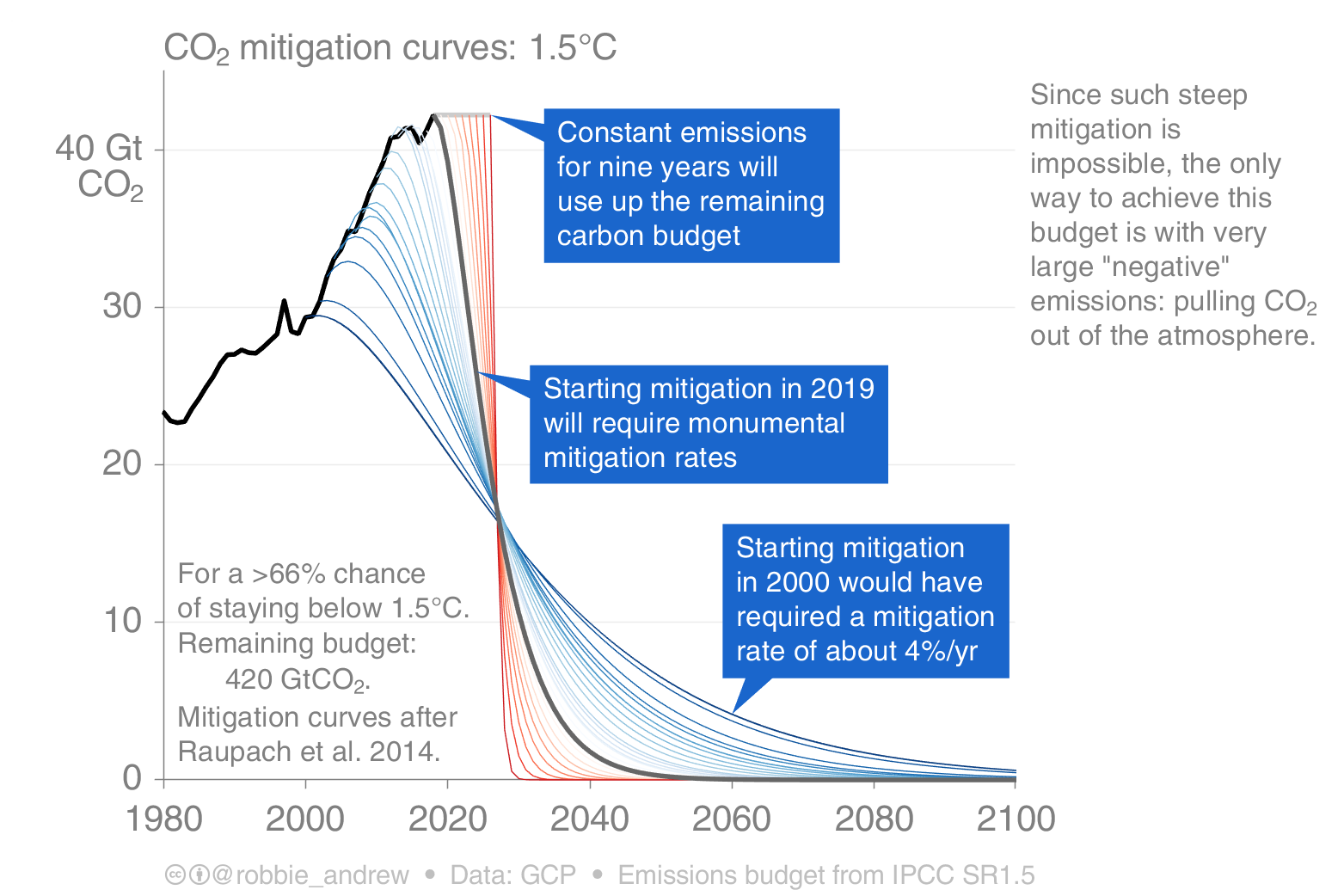
The lack of effective action so far means that high emission countries such as the UK now need to make cuts in CO2 emissions of well over 10% per year, if global warming is to be kept below 1.5°C.
Emission cuts in high-polluting countries
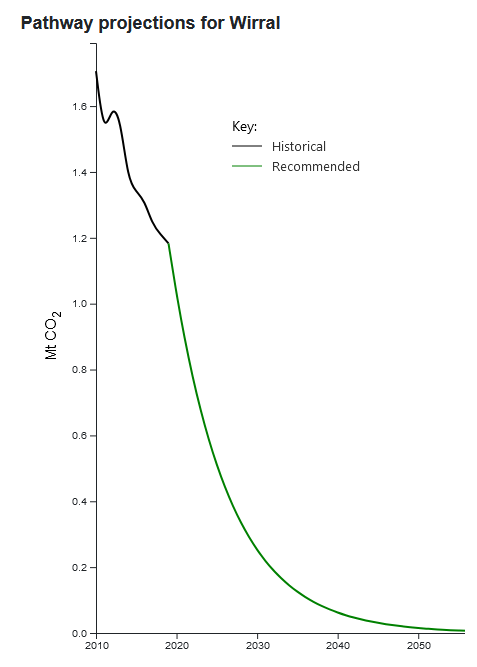 The Tyndall Centre reports: The Tyndall Centre for Climate Change Research at the University of Manchester published calculations in 2019 in reports for each UK local authority [3]. For example, the report for Wirral Council [4] showed that annual cuts in emissions of 13% were needed (with the lack of action, faster cuts are now required). Figure 1 of the report ("Pathway projections for Wirral"), showing the rapid cuts, is reproduced here.
The Tyndall Centre reports: The Tyndall Centre for Climate Change Research at the University of Manchester published calculations in 2019 in reports for each UK local authority [3]. For example, the report for Wirral Council [4] showed that annual cuts in emissions of 13% were needed (with the lack of action, faster cuts are now required). Figure 1 of the report ("Pathway projections for Wirral"), showing the rapid cuts, is reproduced here.References
| [1] | https://folk.uio.no/roberan/img/GCB2018/PNG/s00_2018_Mitigation_Curves_1.5C.png |
| [2] | Figures from Global Carbon Budget 2018 https://folk.universitetetioslo.no/roberan/GCB2018.shtml |
| [3] | Tyndall Centre The Tyndall carbon budget tool (2019) https://carbonbudget.manchester.ac.uk/reports/ |
| [4] | Tyndall Centre (2019) Setting Climate Commitments for Wirral https://carbonbudget.manchester.ac.uk/reports/E08000015/ |
First published: 12 Jul 2023
Last updated: 8 Sep 2023

 ✖
✖